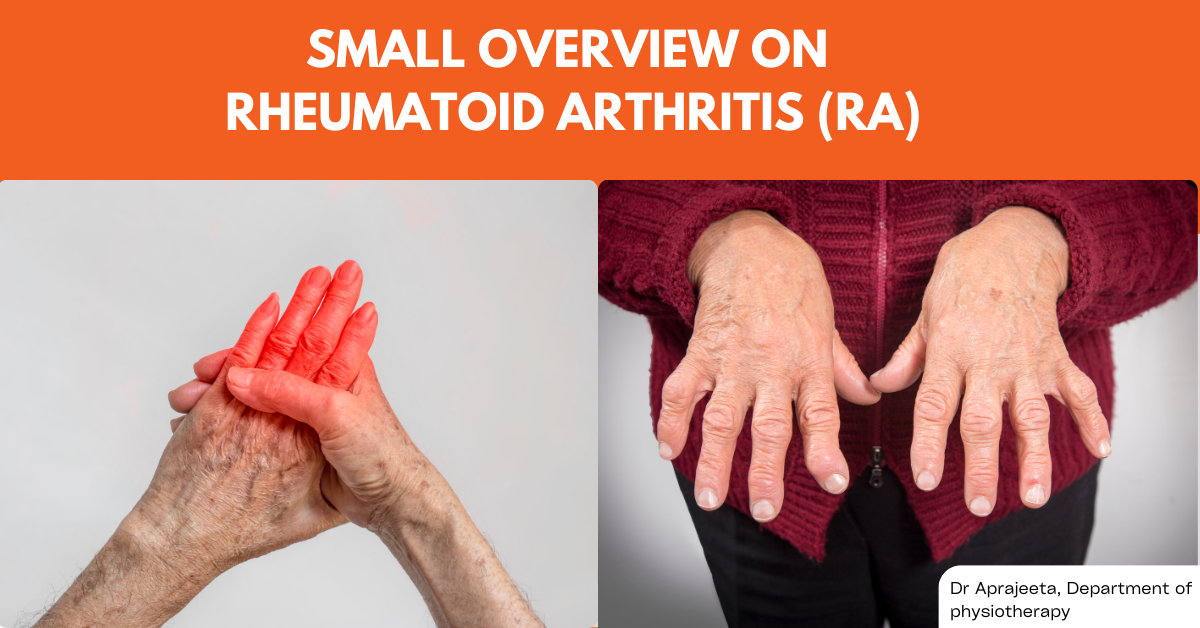
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a relatively common chronic autoimmune disorder. Its prevalence can vary depending on factors such as geographical location, population demographics, and diagnostic criteria. Here is some prevalence information based on available data:
1. Global Prevalence: RA is estimated to affect about 0.5% to 1% of the adult population worldwide. This equates to approximately 5 to 10 million people globally.
2. Regional Variations: The prevalence of RA can vary significantly among different regions and countries. For example, studies have shown higher prevalence rates in Western countries, such as the United States and European nations, compared to some Asian and African countries.
3. Gender Differences: RA is more common in women than in men. Studies indicate that women are two to three times more likely to develop RA than men. However, the reasons for this gender disparity are not fully understood.
4. Age of Onset: Rheumatoid arthritis can start at any age, but it most commonly begins between the ages of 30 and 50. However, there are cases of juvenile-onset RA, which affect children and adolescents.
5. Racial and Ethnic Differences: There may be variations in RA prevalence among different racial and ethnic groups. Some studies have suggested higher rates in certain populations, such as Native Americans and certain Indigenous populations.